Optimization Total Dissolved Gas
This category is added when the Outflow TDG using Tailwater Depth method is selected.
This is the default, no-action method.
This is the optimization component of TDG modeling. See also Total Dissolved Gas Methodology.
This method instantiates the slots and then sets up the data necessary for the Optimization problem. The defining constraints are also described below.
Slots Specific to this Method
Outflow TDG Concentration
Type: Series
Units: Fraction
Description: This slot represents the optimization variable for Outflow TDG Concentration.
Information:
I/O: Set by a rule
Links: Not linkable
Outflow TDG Concentration Estimate
Type: Series
Units: Fraction
Information: The total dissolved gas calculations in Optimization require a prerun estimate of Outflow TDG Concentration at each time step. These values are entered in this series slot, usually by a DMI.
I/O: In the equations, this slot uses the notation: TDGO*
Links: Not linkable
Spill Estimate
Type: Series
Units: FLOW
Description: The total dissolved gas calculations in Optimization require a prerun estimate of Spill at each time step. These values are entered in this series slot, usually by a DMI.
Information: In the equations, this slot uses the notation: QS*
I/O: Input by the user or through a DMI
Links: Not linkable
Spill TDG Concentration
Type: Series
Units: Fraction
Description: This slot represents the optimization variable for Spill TDG Concentration.
Information:
I/O: Set by a rule
Links: Not linkable
Tailwater Elevation Estimate
Type: Series
Units: Length
Description: This slot operates the same as the Spill Estimate slot but for Tailwater.
Information:
I/O: Input by the user or through a DMI
Links: Not linkable
Turbine Release Estimate
Type: Series
Units: Flow
Description: This slot operates the same as the Spill Estimate slot but for Turbine Release.
Information: QT*
I/O: Input by the user or through a DMI
Links: Not linkable
Turbine Release TDG Concentration
Type: Series
Units: Fraction
Description: Optimization variable defined based on the lag from the Inflow TDG Concentration.
Information:
Links:
Turbine Release TDG Concentration Estimate
Type: Series
Units: Fraction
Description: This slot operates the same as the Spill Estimate slot but for Turbine Release TDG Concentration.
Information: This value must be input if you want to write policy constraints on the Turbine Release TDG Concentration.
Links: Not linkable
dSlot1 dSlot2 Partial Derivative Slots
Type: Series Slot
Description: The following table lists all partial derivative slots. They are all individual series slots containing the values computed in the simulation portion and used as input values in the next optimization solution. The table describes the information stored in each column.
The slot name is formed as “the partial of Slot 1 with respect to the partial of Slot 2”; that is, “dSlot1 dSlot2”. The slot names have no spaces and use underscores where appropriate.
I/O: Input (for use in optimization) or Output (computed by WQ methods)
Links: Not linkable
Slot Name | Units | Comment and Equation |
|---|---|---|
dTDG_Outflow dTDG_Spill | None | Partial derivative of Outflow TDG Concentration with respect to Spill TDG Concentration |
dTDG_Outflow dTDG_TurbineRelease | None | Partial derivative of Outflow TDG Concentration with respect to Turbine Release TDG Concentration. |
dTDG_Outflow dSpill | Fraction PerFlow | Partial derivative of Outflow TDG Concentration with respect to Spill. |
dTDG_Outflow dTurbineRelease | Fraction PerFlow | Partial derivative of Outflow TDG Concentration with respect to Turbine Release. |
dTDG_Outflow dEntrainedFlow | Fraction PerFlow | Partial derivative of Outflow TDG Concentration with respect to Entrained Flow. |
dTDG_Outflow dOutflow | Fraction PerFlow | Partial derivative of Outflow TDG Concentration with respect to Outflow. |
dTDG_Spill dTailwater | Fraction PerLength | Partial derivative of Spill TDG Concentration with respect to Tailwater. This is only needed if patm is a series slot. If not, this reduces to a constant. |
dTailwater dTailwaterBaseValue | None | Partial derivative of Tailwater with respect to Tailwater Base Value. Computed based on the selected Tailwater method. |
dTailwater dTailwaterPrevBaseValue | None | Partial derivative of Tailwater with respect to Tailwater Base Value at the previous timestep. Computed based on the selected Tailwater method. |
dTailwater dOutflow | Length PerFlow | Partial derivative of Tailwater with respect to Outflow. Computed based on the selected Tailwater method. |
dPoolElevation dStorage | Length PerVolume | Partial derivative of Pool Elevation with respect to Storage. This value is computed by finding the slope of the Elevation Volume table for the current Pool Elevation/Storage. |
dEntrainedFlow dSpill | None | Partial derivative of Entrained Flow with respect to Spill. |
dEntrainedFlow dTurbineRelease | None | Partial derivative of Entrained Flow with respect to Turbine Release. |
Delta Entrained Flow
Type: Series
Units: Flow
Description: This slot is an optimization variable.
I/O: Output Only
Delta Inflow
Type: Series
Units: Flow
Description: This slot is an optimization variable.
I/O: Output Only
Links: Linkable to upstream Delta Outflow
Delta Outflow
Type: Series
Units: Flow
Information: This slot is an optimization variable.
Links: Linkable to downstream Delta Inflow
Delta Outflow TDG Conc
Type: Series
Units: Fraction
Description: This slot is an optimization variable.
Delta Pool Elevation
Type: Series
Units: Length
Information: This slot is an optimization variable.
Delta Storage
Type: Series
Units: Volume
Information: This slot is an optimization variable.
Delta Spill TDG Conc
Type: Series
Units: Fraction
Information: This slot is an optimization variable.
Delta Tailwater
Type: Series
Units: Length
Information: This slot is an optimization variable.
Delta Tailwater Base Value
Type: Series
Units: Length
Description: This slot is an optimization variable.
Delta Turbine Release TDG Conc
Type: Series
Units: Fraction
Description:
Information: This slot is an optimization variable.
Delta Turbine Release
Type: Series
Units: Fraction
Description:
Information: This slot is an optimization variable.
Method Details
This method is called by the water quality dispatch method and computes the partial derivatives and Taylor expansion equations that will be used in the optimization formulation. This step occurs only when the optimization method is selected, but occurs during water quality dispatching in the simulation runs. In this section, we describe the mathematical formulations but not the order in which they are computed.
To discuss the partial derivatives, we must write the full mathematical representation. In the following description, we show the equations and note where each one is computed: either in the simulation method (Sim Calc or Sim Input) or as a defined variable in the optimization (Defined Variable). That is, within WQ dispatching, the partial derivatives are computed, and then, within the Opt Begin Run, variables are defined as necessary.
Introduce the following variable to track the difference from the estimated value:
TDGO* is the slot Outflow TDG Concentration Estimate - Sim Input
 TDGO is the slot Delta Outflow TDG Concentration - Defined Variable
TDGO is the slot Delta Outflow TDG Concentration - Defined VariableQS is the slot Spill - Defined Variable
QS* is the slot Spill Estimate - Sim Input
QT is the slot Turbine Release - Defined Variable
QT* is the slot Turbine Release Estimate - Sim Input
To write constraints on the Turbine Release TDG Conc, then also track the difference between the estimated concentration and the computed:
TDGO* is the slot Turbine Release TDG Concentration Estimate - Sim Input
The first-order Taylor series approximation is:
The partial derivatives are defined as follows. All of these derivatives are calculated for each timestep and therefore are based on the values computed during the previous rulebased simulation (which used the estimated values, QS*, QT*, and so on).
For low flow conditions, QS and QT < Qsm, alternative partial derivatives are used to improve convergence. The partial derivatives are set based on the ratio = QE / QT. If QT = 0 then ratio = 0.
If TDGT is input, then  TDGT = 0.
TDGT = 0.  TDGI is the Delta Inflow TDG Concentration, which is linked to an upstream object’s
TDGI is the Delta Inflow TDG Concentration, which is linked to an upstream object’s  TDGO slot. The slot Delta Turbine Release TDG Conc is a Defined Variable.
TDGO slot. The slot Delta Turbine Release TDG Conc is a Defined Variable.
Slot: Delta Entrained Flow - Defined Variable
The partials in this equation depend on the condition of Entrained Flow and Turbine Release.
If QE = QT and QT > 0 (using estimated values)
Else
If b3 >= 0 or QE > 0
Else
Next, introduce the variable for the Delta Spill concentration:
To complete the Taylor series expansion:
Slot: Delta Tailwater - Defined Variable
The tailwater partials are based on the selected Tailwater method. The Tailwater is then based on the selected Tailwater Method
• Tailwater Base Value Method
• Base Value Plus Lookup Method
• Stage Flow Method
• Coefficients Table method
If the tailwater base value is input, the partial derivatives are zero. If tailwater base value is set equal to downstream pool elevation then
Res.  TWBV = Downstream(Res).
TWBV = Downstream(Res).  PE, Slot: Delta Tailwater Base Value - Defined Variable
PE, Slot: Delta Tailwater Base Value - Defined Variable
This will require a link, which will create an automatic constraint. The Taylor series equation for pool elevation (aka forebay elevation) depends on reservoir storage.
The partial derivative can be calculated from an elevation-volume table. The dPoolElevation dStorage value is stored in a slot.
Storage is defined by the continuity or mass balance equation:
The partial derivative 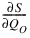 is the length of a time step in the model, dStorage dOutflow. It will initially be implemented as a constant. If a given St is not a variable then
is the length of a time step in the model, dStorage dOutflow. It will initially be implemented as a constant. If a given St is not a variable then  St = 0. For example, S is typically known at the beginning of a model run.
St = 0. For example, S is typically known at the beginning of a model run.
If inflow is equal to an upstream outflow from a reservoir, reach, or confluence then
Res.  QI = UpstreamObj.
QI = UpstreamObj.  QO
QO
Otherwise inflow is an input and as for all inputs,  QI = 0
QI = 0
TDGI is the Inflow TDG Concentration, which is linked to an upstream object’s TDGO slot.
Revised: 08/02/2021