Accounting Diagnostics
Figure 3.14 shows the Post-Simulation Accounting Diagnostics Configuration dialog.
Figure 3.14
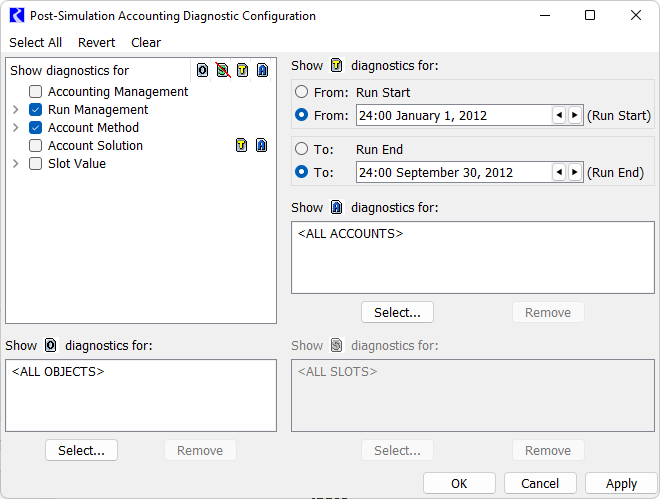
Available filters include Objects, Accounts, Slots, and Timesteps. Diagnostics allow the user to see when each individual account is solving, what slots are known and unknown at that timestep, the accounting method being used, what the value is when an account's slot is set, and more.
Accounting Diagnostic Groups
Table 3.6 summarizes the types of messages that are displayed when a Diagnostic Group is selected.
Super Group | Diagnostics Group | Type of diagnostics issued |
|---|---|---|
Run Management: | ||
Controller | Beginning/End of Run/Timestep for each time. Examples: • Initializing model run. • Beginning of Run. • Begin Timestep. • Execute timestep. • End of run. | |
Object | Beginning/End of Run/Timestep for each Object and time. Examples: • Clear state. • Propagating user input. • Beginning of run. • Begin timestep. • End timestep. • End of run. | |
Account | Beginning of Run for each Account and time. Examples: • Clear state. • Propagating user input. | |
Account Method: | ||
Controller | Describes when the controller is notified of a change to an account's slot. Example: • The "Post-Simulation Accounting" controller received a slot changed notification for slot "BigLake^City.Inflow". | |
Object | Describes which user defined methods are being executed. Example: • Executing Category "Storage Account Gain Loss" with selected method "BigLake_Gain Loss". | |
User Method Execution | Diagnostics for object level accounting methods. Examples: • Executing user-defined accounting method #3 ("HappyLake_SlotInflows", within group "Storage Account Slot Inflow") • Assignment initiated (the left-hand side is "$ "HappyLake^Fish.Slot Inflow" []"). • Evaluation of Assign statement successful; will attempt assignment: Fish.Slot Inflow[January 1, 2004] = 3.99 [1.00 * cfs]. | |
Independent Groups: | ||
Account Management | • N/A | |
Account Solution | Describes when the account is solving including the knowns and unknowns. Example: • Inflow is known, Storage is allowed, Outflow is input; solving for Storage. | |
Slot Value: | ||
Set Value | Describes when an accounting slot is set. Example: • Confluence^Fish.Inflow: Set value = 25.740254 * 1.0cfs | |
Interpolation | Table Slot table interpolation lookups for each account slot. | |
Revised: 01/05/2024